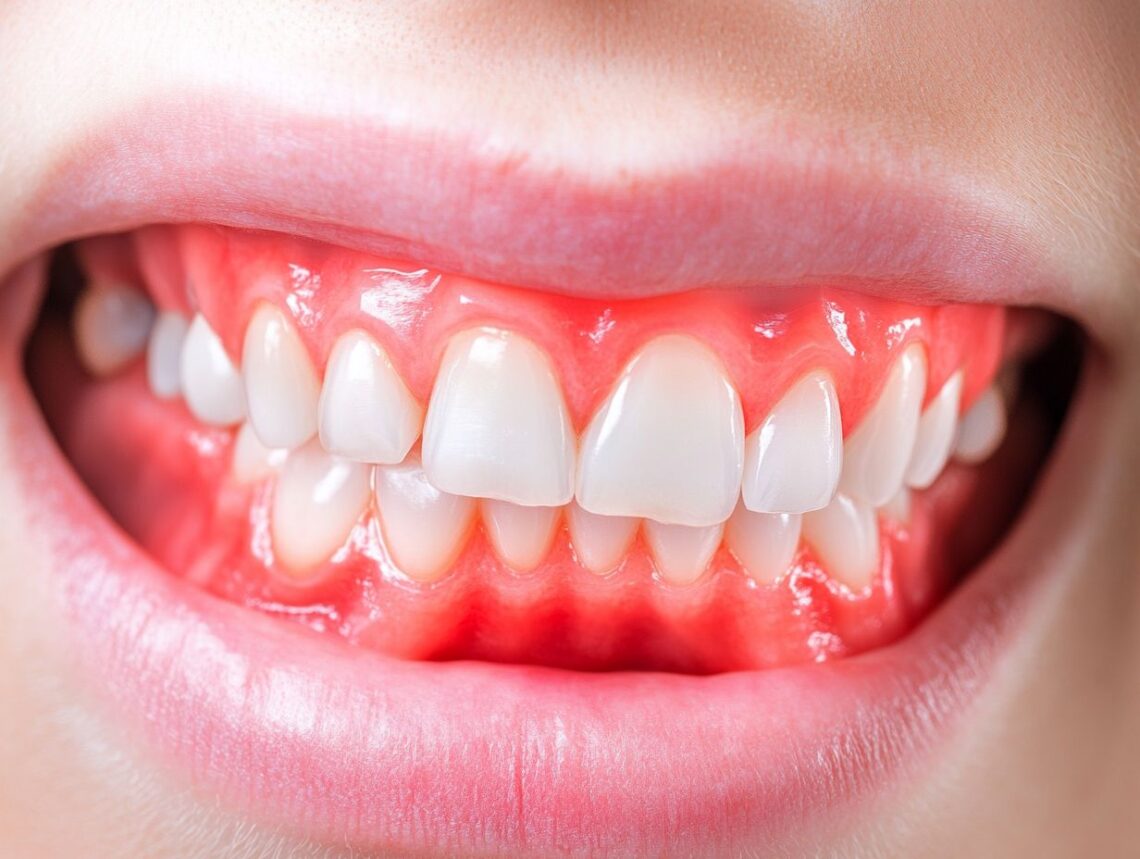
Gum infections may present as an unexpected and concerning outcome of dental cleaning procedures, raising significant questions regarding oral health even following professional treatment.
This article aims to elucidate the nature of gum infections, their underlying causes, and the ways in which they may manifest after a dental visit.
Readers will gain insight into recognizing early warning signs, exploring effective treatment options, and identifying best practices for preventing future infections.
A comprehensive understanding of these factors is essential for maintaining healthy gums and ensuring a confident smile.
Key Takeaways:
Understanding Gum Infection after Teeth Cleaning
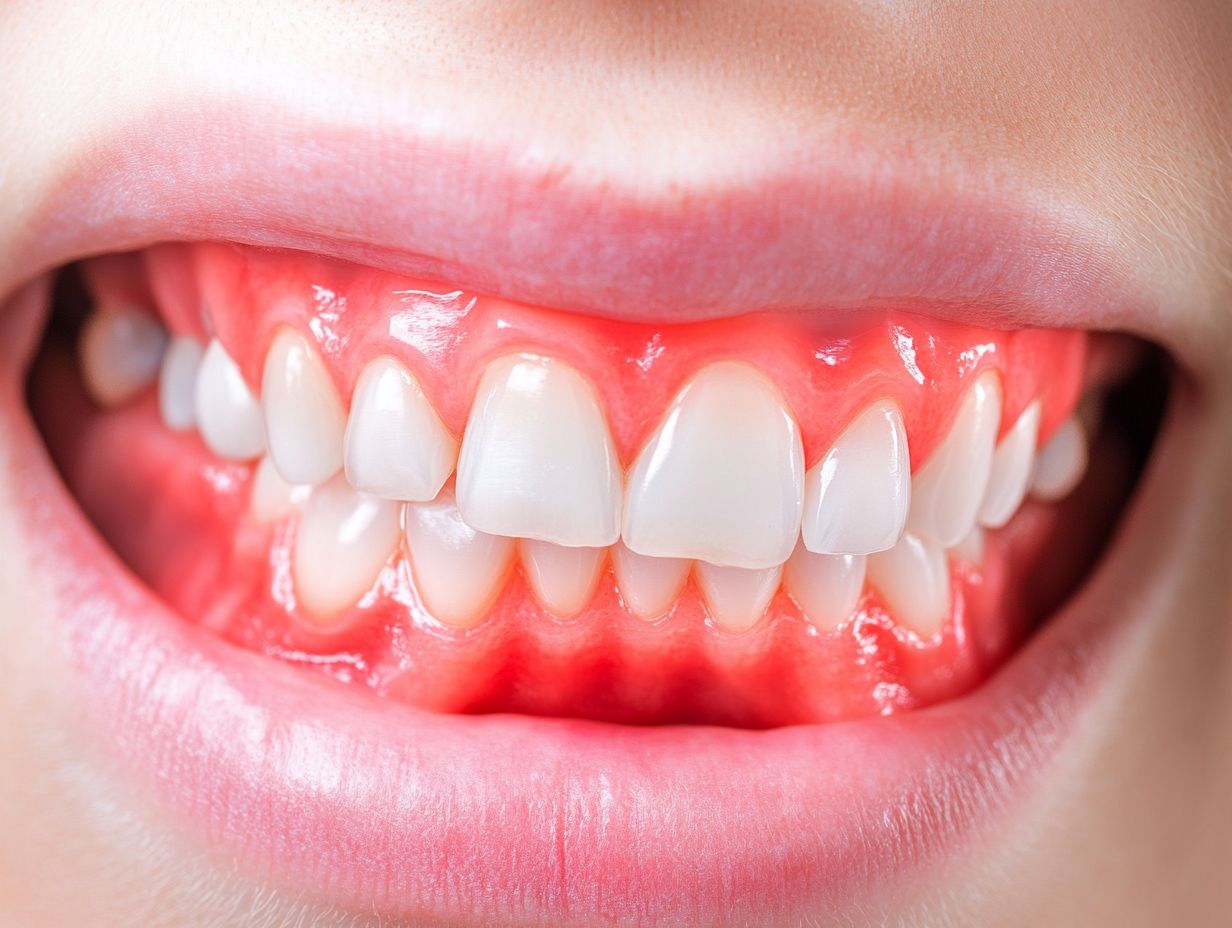
Understanding gum infections following teeth cleaning is essential for maintaining optimal oral health and preventing serious dental complications. These infections can occur due to inadequate dental cleaning procedures, resulting in issues such as plaque and tartar accumulation, gum inflammation, and the exacerbation of existing gum problems.
Dental negligence during routine or deep cleaning procedures by a dental hygienist may leave patients vulnerable to bacterial contamination, leading to mild gum infections that can develop into more severe dental or tooth infections if not promptly addressed. Utilizing proper dental equipment and techniques is essential to avoid these risks.
It is imperative for both patients and dental professionals to recognize the significance of preventive measures and effective treatment for gingivitis to mitigate the potential risks associated with dental prophylaxis.
What is a Gum Infection?
A gum infection, commonly referred to as gingivitis or gum disease, is an inflammatory condition that affects the gums surrounding the teeth.
This concerning oral health issue generally arises from the accumulation of plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that forms on the teeth. When plaque is not adequately removed through regular brushing and flossing, it can harden into tartar, which provides a protective environment for bacteria and exacerbates inflammation.
Symptoms of gum infection may include swollen and bleeding gums, persistent halitosis, and discomfort while chewing. It is essential for individuals to recognize these early signs of gum disease, as untreated infections can progress to more severe conditions, such as periodontitis.
This advanced stage not only jeopardizes the stability of teeth but may also have systemic health implications, potentially affecting overall well-being and leading to conditions such as tooth abscess and gum recession.
Causes of Gum Infection after Teeth Cleaning
Gum infections following teeth cleaning can arise from various factors, including dental negligence that may result in the inadequate removal of plaque and tartar buildup.
When dental professionals do not employ proper techniques during the cleaning process, remnants of plaque can solidify into tartar, which is difficult to eliminate without comprehensive scaling and root planing or gingival curettage. If the cleaning procedure fails to thoroughly address underlying issues, such as bacterial pockets located beneath the gum line, patients may inadvertently increase their risk of infection. In some cases, an antibiotic rinse may be recommended to further combat potential bacterial infections.
Additionally, several factors, including inconsistent oral hygiene practices and pre-existing health conditions, can exacerbate these issues, further complicating the body’s ability to effectively combat infections.
Signs and Symptoms of a Gum Infection
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of a gum infection is essential for timely intervention and effective treatment.
Symptoms may include swelling, redness, and tenderness in the gums, which can indicate gingivitis or a more advanced gum infection. Patients may also experience bleeding during brushing, persistent halitosis, and even tooth pain, all of which are indicators of underlying gum inflammation. In some cases, untreated conditions can progress to periodontitis, a severe form of gum disease.
Early detection is crucial, as untreated gum infections can progress to more serious conditions, such as tooth infections, ultimately affecting overall oral hygiene and health.
Identifying Early Warning Signs
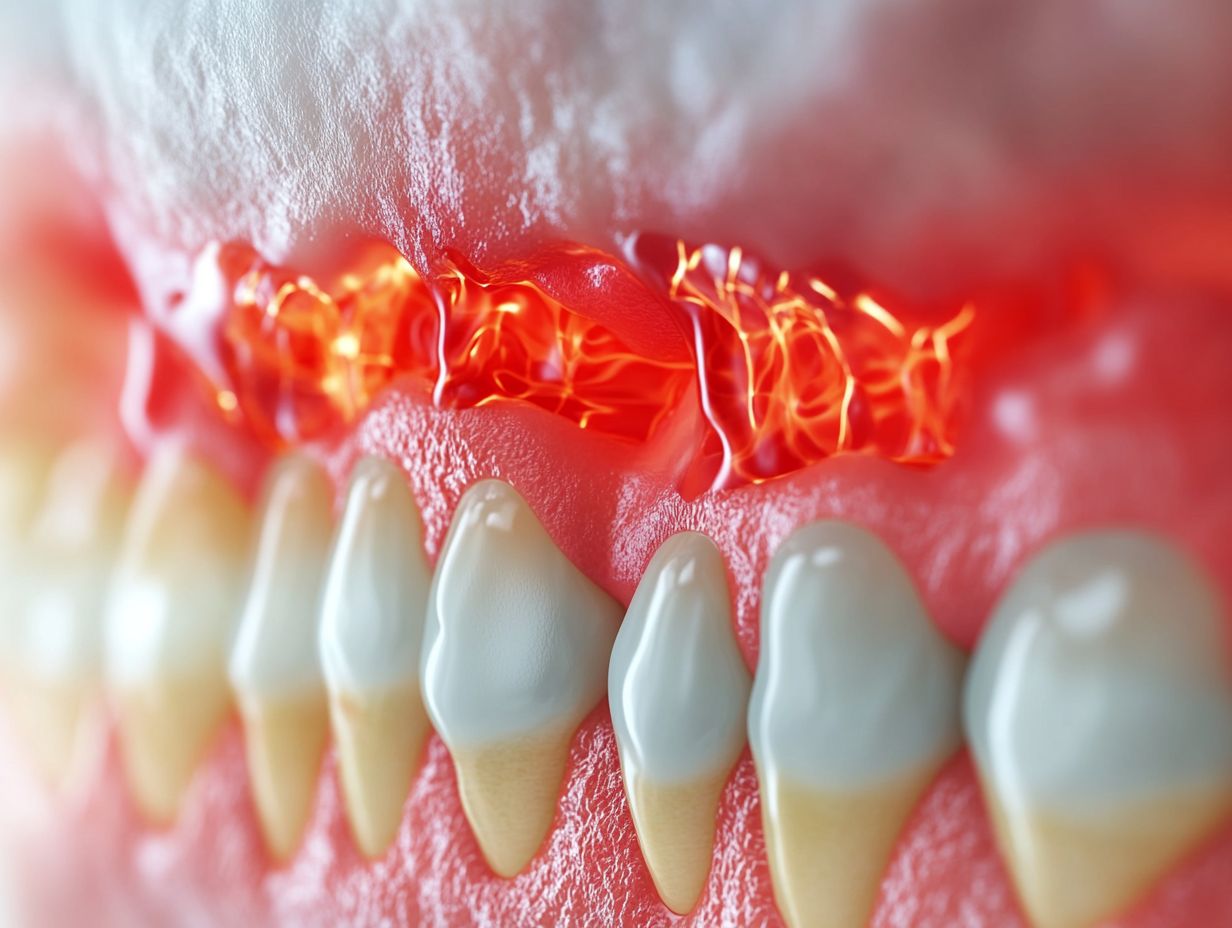
Identifying early warning signs of a gum infection is essential for preventing its progression and maintaining good oral hygiene. These signs often include symptoms such as gum bleeding, sensitivity to hot or cold foods, and persistent bad breath, each serving as a critical indicator of potential underlying issues.
Recognizing these signals early can significantly impact the health of both gums and teeth.
Regular dental checkups are essential; they not only aid in monitoring gum health but also facilitate timely interventions to address any emerging problems. Neglecting these signs could lead to more severe complications, thereby emphasizing the necessity for proactive care in maintaining optimal oral health.
Treatment Options for Gum Infection
Treatment options for gum infections can vary depending on the severity and underlying causes, but they typically include effective gingivitis management and professional dental procedures.
Common approaches often involve scaling and root planing to eliminate plaque and tartar accumulation beneath the gum line, in addition to the application of chlorhexidine rinse to decrease bacterial presence and promote healing. Gingivitis treatment may also include preventive procedures designed to halt the progression of gum disease.
In certain cases, antibiotics may be prescribed to address the dental infection, ensuring that the gum infection is resolved in a timely and effective manner.
Medications and Procedures
Medications and procedures for the treatment of gum infections primarily encompass the use of chlorhexidine rinses and scaling and root planing techniques.
Chlorhexidine is a potent antiseptic that effectively reduces plaque and combats the bacteria responsible for gum disease, making it a fundamental component of dental care routines. Scaling and root planing involve a meticulous cleaning process of the teeth both above and below the gum line, which not only eliminates tartar and bacteria but also smooths the tooth roots to foster healthier gum attachment.
These two approaches function synergistically to address existing infections while preventing recurrences. Additionally, dentists may prescribe antibiotics, such as amoxicillin or metronidazole, to further enhance the body’s ability to heal and control infection.
This underscores the significance of a comprehensive treatment plan in effectively managing gum infections, which may include addressing oral health issues related to dental negligence and utilizing prophylactic measures to prevent future infections.
Preventing Gum Infection after Teeth Cleaning
Preventing gum infections following teeth cleaning is essential for maintaining long-term oral health and mitigating the complications associated with gum disease. Implementing effective preventive measures, such as regular dental cleaning, can significantly decrease the likelihood of developing mild gum infections and other oral health concerns.
This encompasses not only regular dental cleanings but also the adherence to proper oral hygiene practices, such as brushing, flossing, and scheduling routine dental checkups, all of which are fundamental components of a comprehensive oral care regimen.
Best Practices for Oral Hygiene

Implementing best practices for oral hygiene is essential for the prevention of gum infection and the maintenance of overall dental health. This includes not only brushing teeth twice daily with fluoride toothpaste but also integrating flossing into one’s daily routine to effectively remove plaque and food particles from between the teeth.
Adults should allocate a minimum of two minutes for brushing to ensure thorough coverage of all tooth surfaces, while children may benefit from supervised brushing to help establish this important habit at an early age.
The use of an antiseptic mouthwash can further assist in eliminating bacteria, thereby providing additional protection against cavities and bad breath.
Regular dental check-ups, particularly in areas with high standards of care such as Salt Lake City, coupled with educating children about the importance of these oral hygiene practices, can promote a lifetime of robust oral health.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Understanding when to seek medical attention for a gum infection is essential for preventing potential complications, including tooth infections or advanced gum disease.
Patients are advised to consult their dentist if they experience persistent symptoms such as swollen or bleeding gums, chronic bad breath, or pain that does not alleviate.
Additionally, regular dental checkups are critical, as they facilitate the early identification of gum inflammation and enable timely intervention for gingivitis, thereby preventing the progression to more severe conditions.
Indications for Seeking Professional Help
Indications for seeking professional assistance regarding a gum infection include persistent gum bleeding, significant swelling, and recurrent halitosis, which may necessitate immediate intervention.
Furthermore, individuals who experience increased tooth sensitivity or observe a change in the alignment of their teeth should not hesitate to consult a dental professional. These symptoms frequently indicate underlying issues that could escalate into more serious conditions if left unaddressed.
Early detection is crucial in mitigating the progression of gum disease, as timely intervention can prevent further complications, including tooth loss and systemic health issues.
Regular dental check-ups are essential for maintaining overall oral health, as they facilitate the identification of potential problems before they develop into more severe concerns.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a gum infection after teeth cleaning?
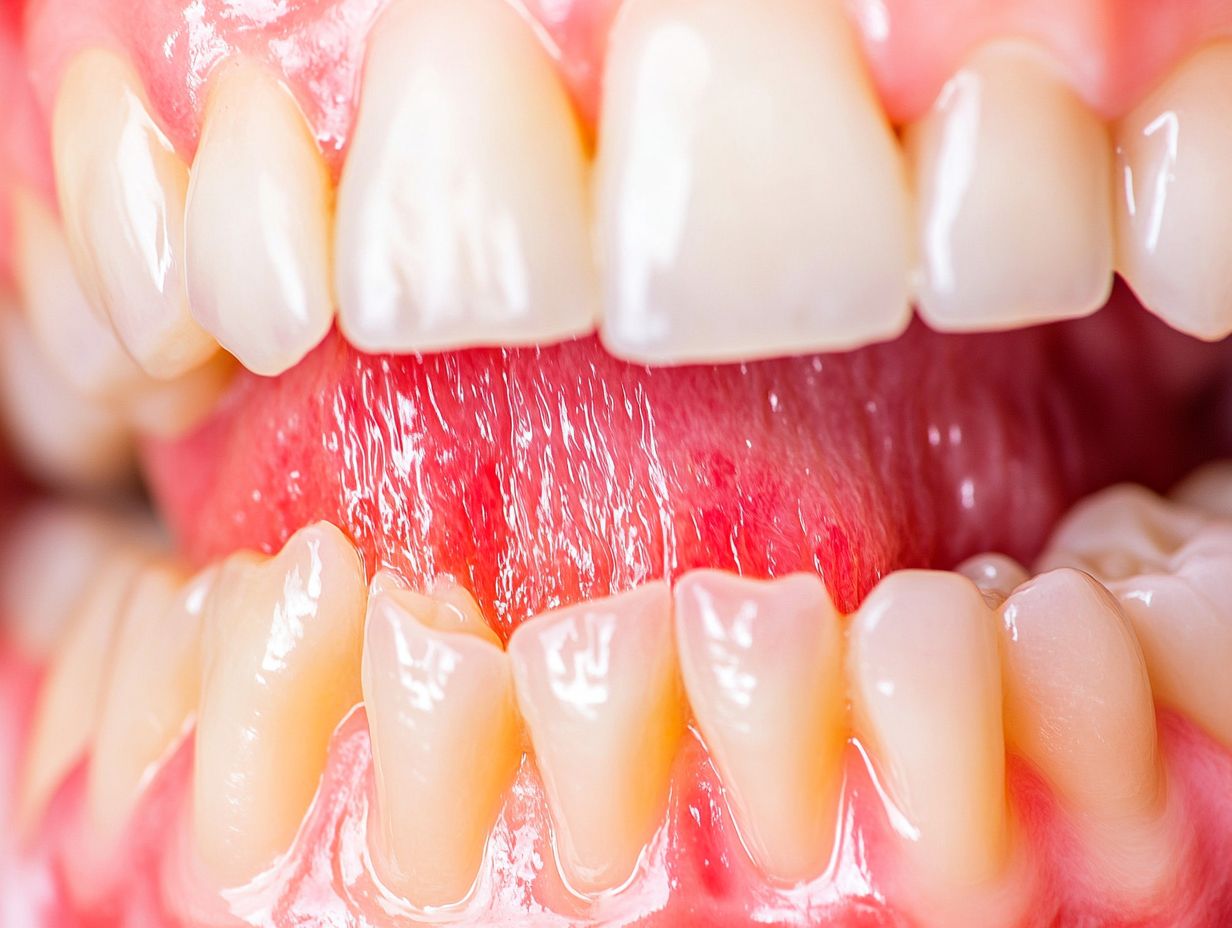
A gum infection after teeth cleaning, also known as periodontal disease, is an infection of the gums that can occur after a dental cleaning. It is caused by bacteria in plaque and tartar buildup and can lead to inflammation and damage to the gums and surrounding tissues. Dental negligence and poor oral hygiene practices can exacerbate these issues, making it crucial to follow preventive procedures.
What are the symptoms of a gum infection after teeth cleaning?
The symptoms of a gum infection after teeth cleaning may include red, swollen, and tender gums, bleeding while brushing or flossing, bad breath, gum recession, and receding gums. In more severe cases, there may also be tooth sensitivity, a tooth infection, or even a tooth abscess, leading to loose or shifting teeth.
How is a gum infection after routine cleaning treated?
Treatment for a gum infection after teeth cleaning may include a deep cleaning procedure called scaling and root planing, which removes plaque and tartar buildup from below the gumline. An antibiotic rinse or chlorhexidine rinse may also be prescribed to reduce bacterial contamination. In more advanced cases, gingival curettage or surgery may be necessary to repair damaged gum tissue and bone.
Can a gum infection after dental cleaning be prevented?
Yes, a gum infection after teeth cleaning can be prevented by maintaining good oral hygiene practices, such as brushing twice a day, flossing daily, and visiting the dental hygienist for regular cleanings and checkups, commonly known as dental prophylaxis. Avoiding tobacco use and eating a balanced diet can also help prevent gum disease and other gum problems like gingivitis and mild gum infections.
Is a gum infection after teeth cleaning contagious?
No, a gum infection after teeth cleaning is not contagious. However, the bacteria that cause gum disease can spread through saliva, so it is important to practice good oral hygiene and avoid sharing toothbrushes or other dental equipment with others to prevent bacterial contamination.
Can a gum infection after teeth cleaning lead to other health problems?
Yes, if left untreated, a gum infection after teeth cleaning can lead to other health problems. This is because the bacteria in the mouth can enter the bloodstream and potentially contribute to heart disease, diabetes, and other systemic health issues. Untreated gum disease can progress to periodontitis, a severe form of gum inflammation, which can further compromise oral health and lead to tooth abscesses. It is important to seek treatment for gum disease to maintain overall health and consider consulting with specialists like the Dental Law Partnership if there is a concern of dental negligence.