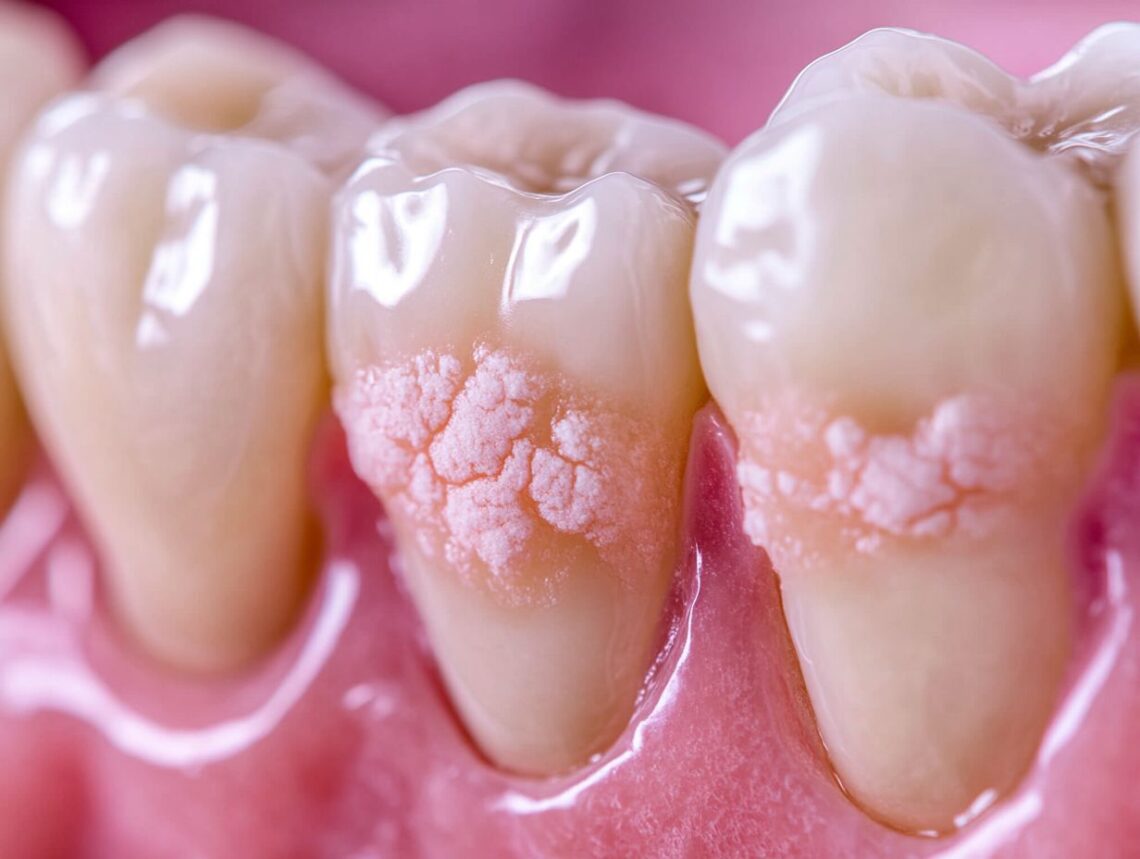
White spot lesions on teeth represent a prevalent dental concern, frequently indicating early signs of enamel demineralization. A comprehensive understanding of these lesions is essential for the maintenance of optimal oral health.
This article aims to elucidate the nature of white spot lesions, their causes and risk factors, as well as the diagnostic process involved. Additionally, it will examine various treatment options, ranging from remineralization techniques to professional dental interventions. Preventive measures and cosmetic solutions to manage the appearance of these lesions will also be discussed.
This exploration serves to provide critical insights into white spot lesions and the strategies to protect one’s smile.
Key Takeaways:
White spot lesions, a common manifestation of dental caries, require prompt diagnosis and treatment for optimal oral health.
Understanding White Spot Lesions on Teeth
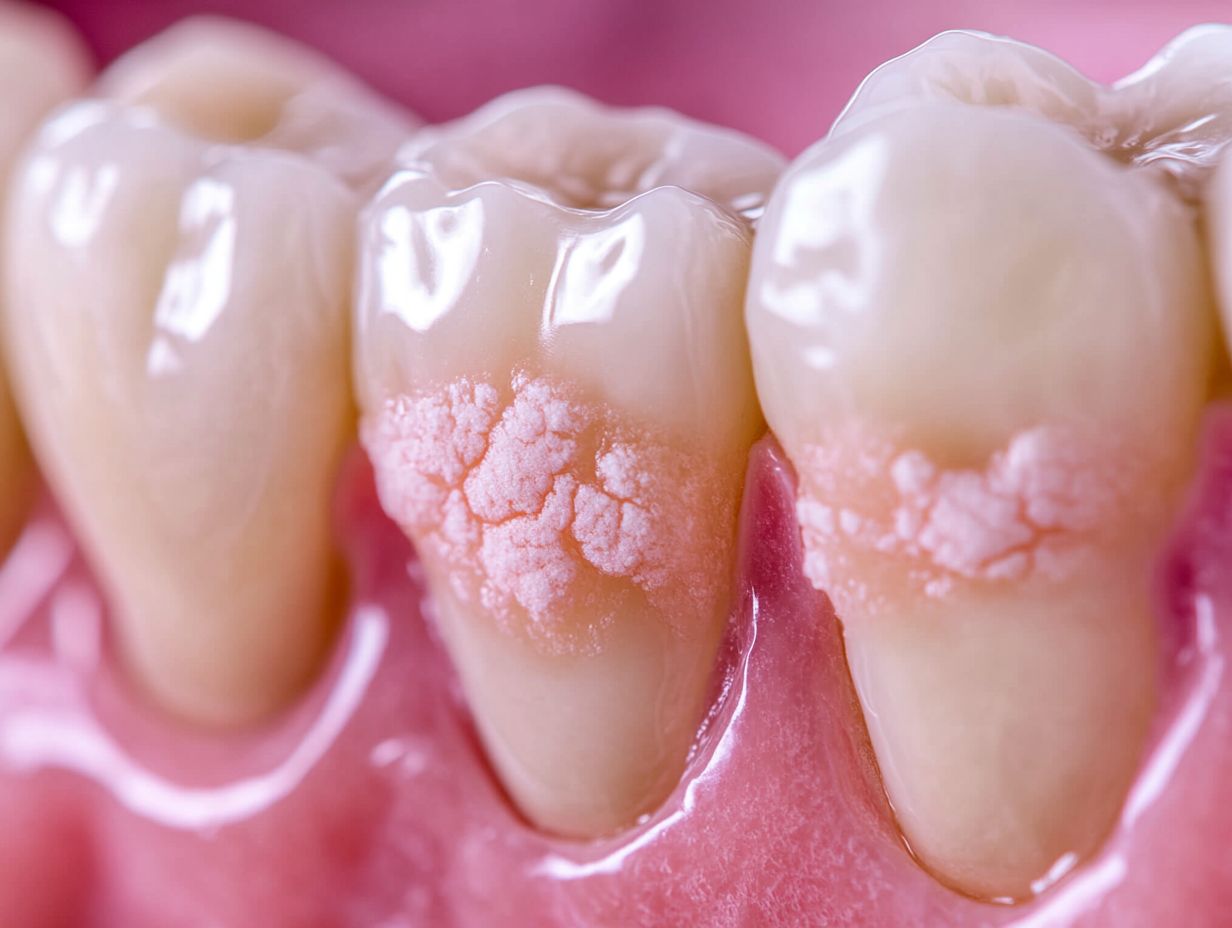
White spot lesions are a prevalent manifestation of dental caries, particularly observed in individuals undergoing orthodontic treatment. These lesions are characterized by their altered optical properties, presenting as opaque white areas on the enamel and signifying underlying demineralization.
A comprehensive understanding of the etiology and clinical implications of white spot lesions is vital for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. This understanding is often informed by systematic reviews and randomized controlled trials, addressing factors such as inadequate oral hygiene and suboptimal dietary habits.
Therefore, it is imperative for dental professionals to adopt systematic reviews and clinical strategies to mitigate the risks associated with these lesions.
What are White Spot Lesions and their Clinical Approaches?
White spot lesions are defined as localized areas of demineralized enamel that exhibit an opaque white appearance, often serving as early indicators of dental caries.
These lesions generally develop on the smooth surfaces of teeth, particularly in regions prone to plaque accumulation, making them a significant concern in pediatric dentistry and orthodontics, where enamel development is crucial.
The appearance of these lesions signifies an imbalance in the oral environment, where factors such as inadequate oral hygiene, high sugar dietary habits, and reduced salivary flow contribute to enamel erosion.
From a clinical perspective, the timely recognition of white spot lesions is imperative, as they represent the initial stages of the carious process, allowing for appropriate interventions.
If left untreated, these lesions can progress to cavitated caries, resulting in more severe dental complications that may require invasive treatments.
Causes and Risk Factors
The development of white spot lesions can be attributed to various factors, including inadequate oral hygiene, dietary habits, and the presence of orthodontic appliances, which may hinder enamel development and elevate the risk of enamel demineralization and porosity.
Insufficient brushing and flossing often fail to eliminate plaque accumulation, allowing bacteria to thrive and produce acids that erode enamel. A diet that is high in sugars and acids can further exacerbate this condition, as such foods create a favorable environment for harmful bacteria. Additionally, orthodontic appliances, such as braces and retainers, can complicate the maintenance of proper oral hygiene, leading to the formation of pockets where plaque may accumulate.
Consequently, this combination of dietary choices and mechanical challenges not only promotes the development of white spot lesions but also highlights the critical need for improved oral care during orthodontic treatment.
Diagnosing White Spot Lesions with Diagnostic Tools and Systematic Review
The effective diagnosis of white spot lesions requires a comprehensive approach that includes both visual examination and the utilization of advanced diagnostic tools, following the guidelines of systematic review methodologies such as PRISMA and considering the risk of bias.
These methods are essential for accurately assessing the extent of demineralization and developing appropriate treatment strategies.
Visual Examination and Advanced Diagnostic Tools
Visual examination remains the foundational method for diagnosing white spot lesions; however, advancements in diagnostic tools, such as fluorescence techniques and devices like DIAGNOdent, microradiography, and computed microtomography, have significantly enhanced detection accuracy.
These innovations facilitate a more nuanced approach, enabling clinicians to assess the presence and extent of lesions that may not be discernible to the naked eye. Microradiography and computed microtomography provide detailed imaging that reveals the mineral content of tooth structure, aiding in the differentiation between active and inactive lesions.
By integrating visual assessments with technological aids, practitioners are better equipped to identify early signs of demineralization, ultimately leading to improved treatment planning and timely interventions.
The adoption of these comprehensive diagnostic methods enables dental professionals to enhance patient outcomes and potentially prevent the progression of caries.
Treatment Options for White Spot Lesions
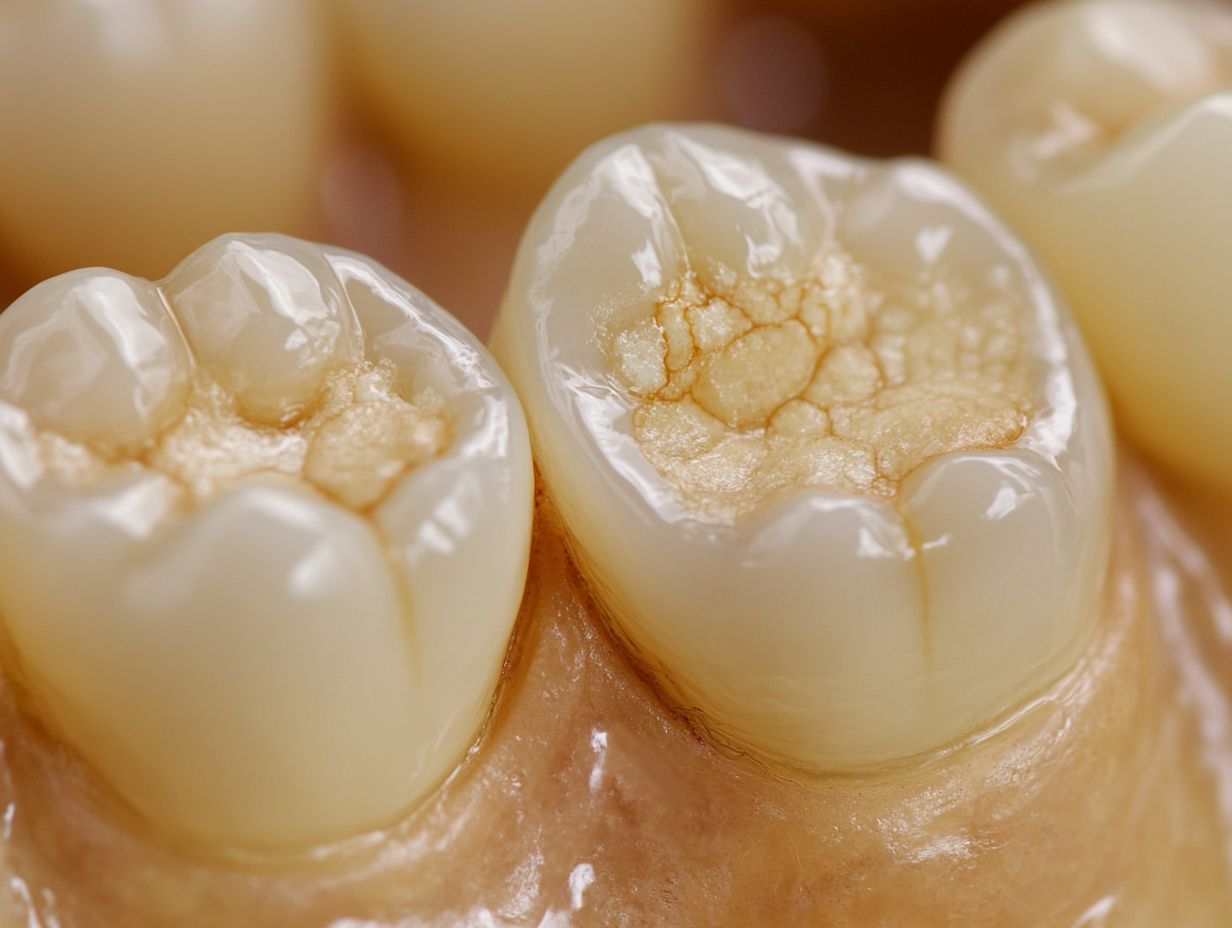
The treatment of white spot lesions encompasses various options, including remineralization techniques that employ fluoride-based products, casein phosphopeptide, and innovative methods such as self-assembling peptide P11-4.
Additionally, more advanced methods, such as resin infiltration, are utilized to restore the integrity of the enamel.
Remineralization Techniques
Remineralization techniques for white spot lesions emphasize the replenishment of lost minerals in the enamel, primarily through the application of fluoride-based products and innovative agents such as casein phosphopeptide and self-assembling peptide P11-4.
These methods are essential in clinical practice, as they enhance the natural repair processes of enamel following demineralization. Fluoride-based treatments, including varnishes and gels, facilitate the deposition of minerals back into the enamel structure, thereby effectively reversing the early stages of decay. Additionally, by forming a protective layer on the teeth, fluoride aids in the prevention of further demineralization.
Conversely, casein phosphopeptide, which is derived from milk protein, functions by stabilizing calcium and phosphate ions, thereby increasing their availability during the mineralization process. Research has demonstrated that these remineralization techniques can significantly mitigate the progression of white spot lesions, with fluoride exhibiting up to a 30% improvement in enamel hardness compared to traditional treatments.
Collectively, these approaches represent a promising avenue for enhancing oral health and preserving the integrity of teeth.
Professional Dental Treatments
Professional dental treatments for white spot lesions commonly involve the application of infiltrating resin, casein phosphopeptide-amorphous calcium phosphate, or hydrochloric acid-based solutions, which serve to halt the progression of the condition and enhance the cosmetic appearance of the affected enamel.
This innovative approach has gained significant attention due to its minimally invasive nature, allowing for the preservation of the natural tooth structure while effectively addressing aesthetic concerns.
During the treatment, the clinician carefully prepares the enamel surface and applies the resin, which penetrates the porous areas of the white spot lesions. With proper curing, this process not only improves the visual appeal but also strengthens the enamel, reducing its susceptibility to further demineralization.
Patients typically report high satisfaction rates following the procedure, as their smiles achieve a more uniform and healthy appearance, underscoring the considerable benefits of this targeted intervention.
Preventing White Spot Lesions
Preventing white spot lesions is of paramount importance and can be effectively accomplished through a combination of appropriate oral hygiene practices, informed by systematic reviews and clinical approaches, and dietary modifications designed to mitigate risk factors associated with enamel demineralization.
Oral Hygiene Practices
Implementing effective oral hygiene practices is a critical preventive strategy against white spot lesions, as these practices support optimal enamel development and reduce the risk of dental caries.
By adhering to a consistent routine that includes proper brushing and flossing techniques, individuals can significantly improve their dental health and aid in the caries identification process.
Utilizing a soft-bristled toothbrush, for example, ensures that the enamel remains intact while effectively removing plaque and food particles. It is essential to brush for a minimum of two minutes, ensuring all surfaces of the teeth, including the gumline where bacteria frequently accumulate, are thoroughly cleaned.
Daily flossing is equally important in preventing the buildup of plaque between the teeth, an area that toothbrushes may not adequately reach. Together, these practices not only enhance enamel integrity but also contribute to overall oral health, thereby reducing the likelihood of cavities and the formation of white spot lesions.
Dietary Changes

Implementing dietary changes can significantly reduce the risk of developing white spot lesions by minimizing the consumption of sugary and acidic foods that contribute to enamel demineralization.
By avoiding snacks high in refined sugars and acidic beverages, individuals can strengthen their enamel against damaging pH levels. Emphasizing foods that are rich in calcium and phosphate, such as leafy greens, dairy products, and nuts, is essential for enhancing remineralization processes.
Incorporating whole fruits and vegetables provides fibrous benefits that assist in cleansing the teeth while delivering essential vitamins. Additionally, opting for water instead of sugary drinks is a pivotal strategy that supports overall oral health and helps prevent dental caries.
By making these deliberate food choices, individuals not only protect themselves against the formation of white spot lesions but also promote a stronger, healthier smile. These choices are part of maintaining good oral hygiene and overall dental health.
Managing the Appearance of White Spot Lesions: Clinical Approaches and Diagnostic Tools
The management of white spot lesions can be effectively addressed through a range of cosmetic options and professional dental treatments, with the objective of enhancing the aesthetic quality of teeth impacted by enamel demineralization and the optical properties of enamel.
Cosmetic Options
Cosmetic options for addressing white spot lesions typically involve the application of infiltrating resin, which not only enhances the aesthetic appearance but also fortifies the enamel structure. Additional methods include the use of casein phosphopeptide-amorphous calcium phosphate (CPP-ACP) to remineralize the enamel.
This minimally invasive procedure is increasingly preferred due to its dual benefits: it effectively conceals unsightly spots while simultaneously stabilizing the tooth’s surface. By meticulously infiltrating the porous enamel, this resin penetrates the lesion, achieving a seamless integration with the surrounding tooth structure.
This cosmetic intervention should not be viewed as an isolated solution; rather, it is an integral component of a comprehensive dental treatment plan that may also encompass fluoride varnishing, orthodontic adjustments, or the use of self-assembling peptide P11-4 for enamel restoration.
The efficacy of infiltrating resin in restoring a natural appearance and promoting oral health contributes to its popularity among dental professionals and patients alike. However, it is crucial to use systematic review and randomized controlled trials to evaluate the long-term benefits of these treatments.
For more detailed information, you can refer to resources like BMC Oral Health, which provides systematic searches and data from randomized controlled trials on dental treatments and orthodontic treatment plans.
Frequently Asked Questions: Diagnosis and Treatment of White Spot Lesions
What are white spot lesions on teeth? Understanding Dental Caries and Enamel Demineralization
White spot lesions on teeth are areas of demineralization that appear as chalky white patches on the surface of teeth. They are the earliest sign of tooth decay and can lead to cavities if left untreated. These lesions are often detected through visual examination and diagnostic tools such as DIAGNOdent and microradiography.
What causes white spot lesions on teeth? Identifying Risks and Contributing Factors
White spot lesions on teeth are caused by a build-up of plaque and bacteria on the teeth. This can occur due to poor oral hygiene, excess consumption of sugary or acidic foods and drinks, or certain medical conditions. Orthodontic appliances can also contribute to the formation of these lesions if proper care is not taken.
How can I prevent white spot lesions on teeth? Effective Strategies for Oral Health
The best way to prevent white spot lesions on teeth is to maintain good oral hygiene habits, including brushing twice a day, flossing daily, and visiting the dentist regularly. Avoiding sugary and acidic foods and drinks can also help prevent these lesions. The use of fluoride-based products and casein phosphopeptide can aid in the prevention of enamel demineralization.
Can white spot lesions on teeth be treated? Exploring Treatment Options
Yes, white spot lesions on teeth can be treated. In the early stages, they can be reversed with proper oral hygiene and fluoride treatments. In more advanced cases, the lesions may need to be filled with a dental filling or treated with a dental sealant. Clinical approaches such as the application of infiltrating resin and the use of computed microtomography for detailed assessment can also be effective.
Are white spot lesions on teeth dangerous? Assessing the Risks
While white spot lesions on teeth may not be immediately dangerous, they can lead to cavities and other oral health issues if left untreated. It is important to address these lesions early on to prevent further damage to the teeth. The use of diagnostic tools and systematic review of treatment methods can help in assessing and mitigating risks.
Can white spot lesions on teeth be a sign of something more serious? Investigating Underlying Conditions
In some cases, white spot lesions on teeth can be a sign of an underlying medical condition, such as celiac disease or enamel hypoplasia. It is important to consult with a dentist if you notice these lesions on your teeth to determine the cause and appropriate treatment. A comprehensive diagnosis and treatment plan, following PRISMA guidelines and considering Pubmed and Scopus resources, is essential for effective management.